


Define organic.
Compounds containing carbon that are found in living organisms, except hydrogencarbonates, carbonates and oxides, are organic.2.2.2 Draw the basic structure of a generalized amino acid.
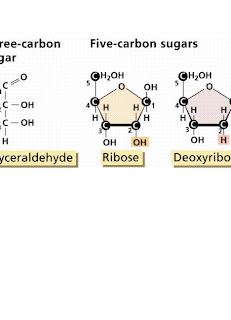
2.2.3 Draw the ring structure of glucose and ribose.
2.2.3 Draw the ring structure of glucose and ribose.
Ribose - given
Glucose - given
Glucose - given
2.2.4 Draw the structure of glycerol and a generalized fatty acid.
2.2.5 Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides; fatty acids, glycerol and glycerides; amino acids, dipeptides and polypeptides.
For monosaccharides, fatty acids, and amino acids to become disaccharides, glycerol, and didpeptides, a condensation reaction needs to occur. When these monomers covalently bond, a water molecule is released; this is a condesation reaction. When many monomers join together through condensation reactions, polymers result. In a hydrolysis reaction, the addition of a water molecule breaks down the covalent bonds and polymers break down into monomers.
2.2.6 Draw the structure of a generalized dipeptide, showing the peptide linkage.
Drawing will be inserted at a later date.
Drawing will be inserted at a later date.
2.2.7 List two examples for each of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Two examples of monosaccharides are glucose and fructose. Two examples of disaccharides are maltose and lactose. Two examples of polysaccharides are starch and cellulose.
Two examples of monosaccharides are glucose and fructose. Two examples of disaccharides are maltose and lactose. Two examples of polysaccharides are starch and cellulose.
2.2.8 State one function of a monosaccharide and one function of a polysaccharide.
One function of a monosaccharide is that they are major nutrients for the cell. One function of a polysaccharide is that provide structural support for the cell.
One function of a monosaccharide is that they are major nutrients for the cell. One function of a polysaccharide is that provide structural support for the cell.
2.2.9 State three functions of lipids.
One function of lipids is that they are great insulators. Also, some lipids function as hormones. In addition, lipids are used for long term energy storage.
2.2.10 Discuss the use of carbohydrates and lipids in energy storage.
The use of carbohydrates in energy storage is through its sugar polymers, glycogen in animals and starch in plants. These sugars are released when the demand for sugar increases. Animals use lipids, mainly fats, for long-term energy storage.
The use of carbohydrates in energy storage is through its sugar polymers, glycogen in animals and starch in plants. These sugars are released when the demand for sugar increases. Animals use lipids, mainly fats, for long-term energy storage.
No comments:
Post a Comment